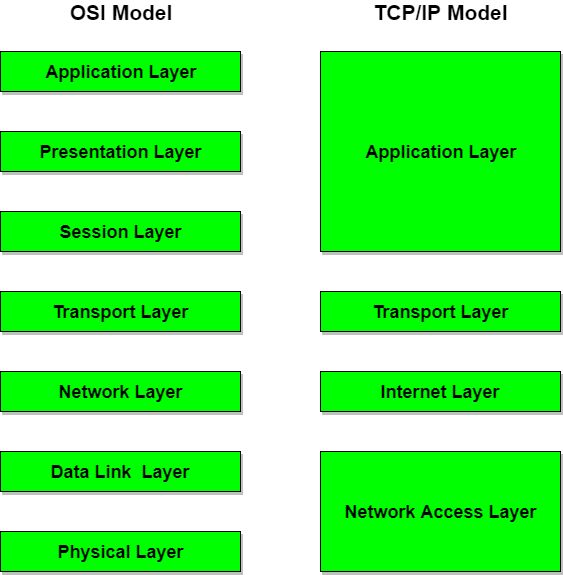
OSI(Open System Interconnection) | TCP/IP(Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol) |
|---|
1. OSI is a generic, protocol independent standard, acting as a communication gateway between the network and end user. | 1. TCP/IP model is based on standard protocols around which the Internet has developed. It is a communication protocol, which allows connection of hosts over a network. |
2. In OSI model the transport layer guarantees the delivery of packets. | 2. In TCP/IP model the transport layer does not guarantees delivery of packets. Still the TCP/IP model is more reliable. |
3. Follows vertical approach. | 3. Follows horizontal approach. |
4. OSI model has a separate Presentation layer and Session layer. | 4. TCP/IP does not have a separate Presentation layer or Session layer. |
5. Transport Layer is Connection Oriented. | 5. Transport Layer is both Connection Oriented and Connection less. |
6. Network Layer is both Connection Oriented and Connection less. | 6. Network Layer is Connection less. |
7. OSI is a reference model around which the networks are built. Generally it is used as a guidance tool. | 7. TCP/IP model is, in a way implementation of the OSI model. |
8. Network layer of OSI model provides both connection oriented and connectionless service. | 8. The Network layer in TCP/IP model provides connectionless service. |
9. OSI model has a problem of fitting the protocols into the model. | 9. TCP/IP model does not fit any protocol |
10. Protocols are hidden in OSI model and are easily replaced as the technology changes. | 10. In TCP/IP replacing protocol is not easy. |
11. OSI model defines services, interfaces and protocols very clearly and makes clear distinction between them. It is protocol independent. | 11. In TCP/IP, services, interfaces and protocols are not clearly separated. It is also protocol dependent. |
12. It has 7 layers | 12. It has 4 layers |

0 Comments